reading-notes
Lists
HTML provides us with three different types of list
1- Ordered lists : are lists where each item in the list is numbered.
2- Unordered lists : are lists that begin with a bullet point
3- Definition lists : are made up of a set of terms along with the definitions for each of those terms.
Lists can be nested inside one another.
Boxes
every element on a page is a rectangular box and we can modify it as desired
1- Box dimensions
2- Limiting Width and Height ( max - min)
3- Overflowing Contect (hidden - scroll)
4- Border, Margin & Padding
Legibility can be improved by controlling the width of boxes containing text and the leading
CSS3 has introduced the ability to create image borders and rounded borders.
ARRAYS
An array is a special type of variable. It doesn’t just store one value; it stores a list of values.
and we can using an array whenever you are working with a list or a set of values that are related to each other.
ACCESSING & CHANGING VALUES IN AN ARRAY
Create the array var colors = [‘white’,’black’ ,’custom’];
Update the third item in the array colors[2] = ‘beige ‘ ;
Get the element with an id of colors var el = document .getElementByid(‘ colors’) ;
Replace with third item from the array el .textContent = colors[2];
Decision and looping
IF … ELSE STATEMENTS
_24Feb17_1750.png) Here, a user can decide among multiple options.The if statements are executed from the top down. As soon as one of the conditions controlling the if is true, the statement associated with that if is executed, and the rest of the ladder is bypassed. If none of the conditions is true, then the final else statement will be executed.
Here, a user can decide among multiple options.The if statements are executed from the top down. As soon as one of the conditions controlling the if is true, the statement associated with that if is executed, and the rest of the ladder is bypassed. If none of the conditions is true, then the final else statement will be executed.
SWITCH STATEMENTS

A switch statement starts with a variable called the switch value. Each case indicates a possible value for this variable and the code that should run if the variable matches that value.
WHILE Loop
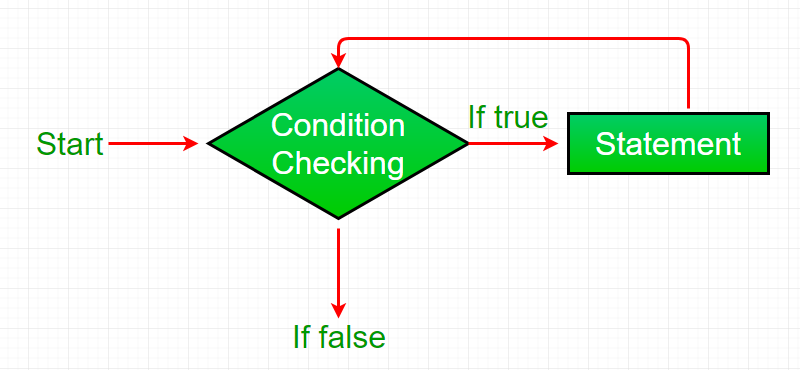 while loop is used when the block of code is to be executed as long as the specified condition is true.
while loop is used when the block of code is to be executed as long as the specified condition is true.
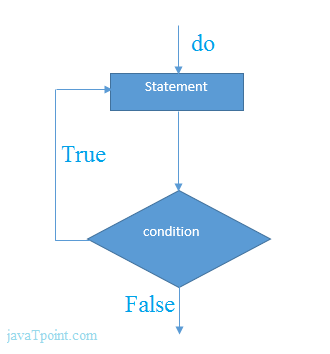
DO WHILE LOOPS
The key difference between a whi 1 e loop and a do whi 1 e loop is that the statements in the code block come before the condition. This means that those statements are run once whether or not the condition is met.